What Information Does the Latent Heat of Vaporization Give
When latent heat is added no temperature change occurs. The enthalpies of vaporization are usually measured at the normal boiling point for that substance.
What Is The Difference Between Latent Heat Of Vaporation And Fusion Quora
This function leads to a graphical correlation which utilizes the slope M of the vapor-pressure curve at the critical point.
. The latent heat. The enthalpy of vaporization ΔHv is additionally named the latent heat of vaporization. Latent originates from the Latin word latere which intends to lie covered up or hid.
The latent heat of vaporization is higher than the latent heat of fusion since gas molecules have the largest intermolecular space and the force of attraction. What information does the latent heat of vaporization give. This heat is required apart from the heat given to melt or vaporize the substance and it works without.
This explains the concept of latent heat which is the extra heat required to change the state of a substance for example if a substance is in the solid-state latent heat provides the extra energy to change its state to liquid and then from the liquid state to the gaseous state. By clicking Accept you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. Latent Heat of Vaporization.
The energy needed to completely melt a mole of a solid B. However the decrease in enthalpy. Similarly the latent heat of vaporization or evaporation L v is the heat that has to be given to a unit mass of material to convert it from the liquid to the vapor phase without a change in temperature.
In case of liquid to gas phase change this amount of energy is known as the enthalpy of vaporization symbol Hvap. This energy breaks down the intermolecular attractive forces and also must provide the energy necessary to expand the gas the pΔV work. Latent heat of vaporization is the heat consumed or discharged when matter disintegrates changing stage from fluid to gas stage at a consistent temperature.
What is meant by specific latent heat of vaporization of water is -226mjkg-1 or -226mjkg. The correlation gives the latent heat of vaporization at any tem-. The latent heat of vaporization supplies theliquid water molecules with enough energy to become vapormolecules.
Why latent heat of vaporization of water is high. The energy needed to completely vaporize a mole of a liquid C. We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits.
The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of a vapor 1C. The energy needed to heat a liquid from freezing point to boiling point D. Latent heat of vaporization of Titanium is 421 kJmol.
Latent heat of vaporization is the heat consumed or discharged when matter disintegrates changing stage from fluid to gas stage at a consistent temperature. The latent heat of vaporization is the heat absorbed or released when matter vaporizes changing phase from liquid to gas phase at a constant temperature. Tetrachloromethane carbon tetrachloride AH 2178 Jg The characteristic properties of the three liquids are given in the table below.
The units are usually Jmol. An example is when the cooling effects of vaporization controls. Required information The latent heats of vaporization for three pure liquids at 0C are given below.
The heat of vaporization is latent heat. Chloroform AH 2709 J-g- 2. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the.
Latent heat is the extra heat required to change the condition of a substance from solid to fluid at its softening point or from fluid to gas at its breaking point after the temperature of the substance has come to both of these focuses. If we add heat continuously as in Figure 1 a change of phase from solid to liquid and then from liquid to vapor occurs. Methanol AH 11895 Jq-1 3.
The latent heat absorbed during the liquid-vapor transition is. Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a change in phase. For the water substance at 1 atm and 100 C the boiling point of water at 1 atm the latent heat of vaporization is 225 10 6 J kg 2 1.
Although sensible heat is often called latent heat it isnt a constant-temperature situation nor is a phase change involved. Now in general when you decrease the pressure enthalpy of both vapor and liquid decreases. The energy needed to heat a liquid from freezing point to boiling.
What information does the latent heat of vaporization give. The energy needed to completely melt a mole of a solid. The difference in enthalpy of vapor and liquid at saturation temperature is defined as LATENT HEAT.
The Enthalpy of vaporization also called the latent heat of vaporization is the change in the enthalpy needed to change an amount of liquid into a gas. And ΔHv is the distinction between the enthalpy of the soaked fume and that of the immersed fluid at a similar. The latent heat of vaporization at 10 atmospherepressure is about 1000 Btu per lbm.
J also known as the latent heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation. It happens at a given pressure. The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of a vapor 1C.
Tional relationship between latent heat of vaporization and reduced temperature and pressure. In physics these changes are examples of phase transitions.

Science Universe Physics Articles Latent Heat Of Vaporization And Of Fusion Explained By The Kinetic Theory

What Does The Latent Heat Of Vaporization Measure Lisbdnet Com

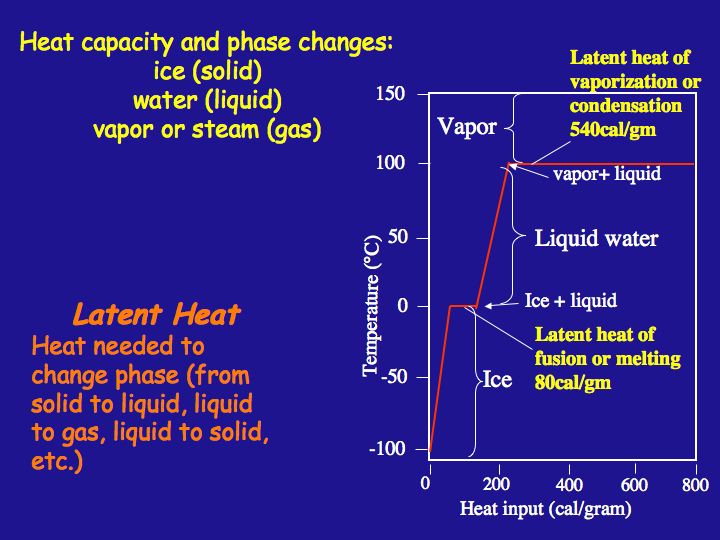
Latent Heat Heat Capacity Earth 540 Essentials Of Oceanography For Educators
No comments for "What Information Does the Latent Heat of Vaporization Give"
Post a Comment